Permainan Maut on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Surakarta is a little-known Indonesian
Surakarta is a little-known Indonesian
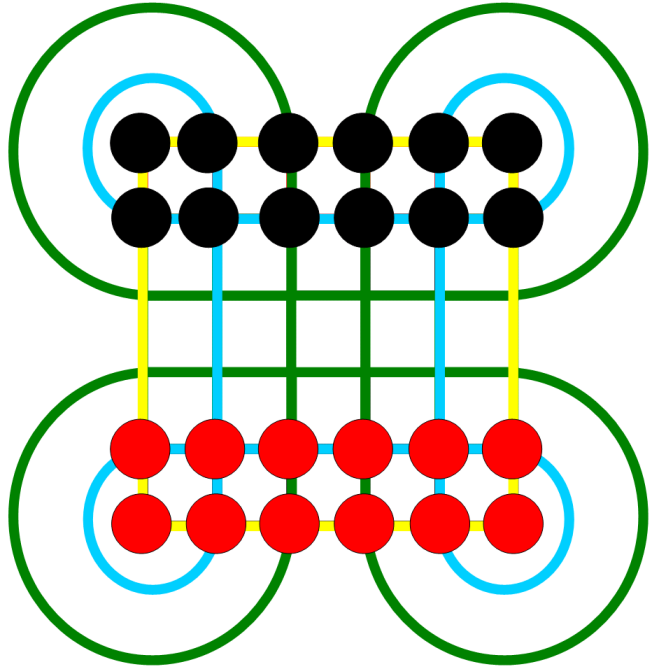
 Traditional Indonesian game pieces are shells versus pebbles or stones, with the board grid inscribed in sand or volcanic ash. But any easily distinguished sets of pieces may be used (e.g. distinguished by colour, as shown). Players begin the game with 12 pieces each.
Traditional Indonesian game pieces are shells versus pebbles or stones, with the board grid inscribed in sand or volcanic ash. But any easily distinguished sets of pieces may be used (e.g. distinguished by colour, as shown). Players begin the game with 12 pieces each.
Surakarta
for Android
Khamadi et al, Perancangan Konsep Adaptasi Permainan Tradisional Bas-Basan Sepur Dalam Permainan Digital "Amukti Palapa"
Abstract strategy games Traditional board games Indonesian inventions Indonesian traditional games
 Surakarta is a little-known Indonesian
Surakarta is a little-known Indonesian strategy
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art ...
board game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well.
Many board games feature a comp ...
for two players, named after the ancient city of Surakarta
Surakarta ( jv, ꦯꦸꦫꦏꦂꦠ), known colloquially as Solo ( jv, ꦱꦭ; ), is a city in Central Java, Indonesia. The 44 km2 (16.2 sq mi) city adjoins Karanganyar Regency and Boyolali Regency to the north, Karanganyar Regency and Sukoh ...
in central Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
. The game features an unusual method of capture which is "possibly unique" and "not known to exist in any other recorded board game". Little is known about its history.
The name of the game in the Indonesian language
Indonesian ( ) is the official language, official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standard language, standardized variety (linguistics), variety of Malay language, Malay, an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that has be ...
is permainan, which simply translates as "the game". In Java, the game is also called ''dam-daman''. It was first published in France in 1970 as "Surakarta". The game is called "Roundabouts" in Sid Sackson's ''The Book of Classic Board Games''.
Equipment
 Traditional Indonesian game pieces are shells versus pebbles or stones, with the board grid inscribed in sand or volcanic ash. But any easily distinguished sets of pieces may be used (e.g. distinguished by colour, as shown). Players begin the game with 12 pieces each.
Traditional Indonesian game pieces are shells versus pebbles or stones, with the board grid inscribed in sand or volcanic ash. But any easily distinguished sets of pieces may be used (e.g. distinguished by colour, as shown). Players begin the game with 12 pieces each.
Rules
Players decide who moves first, then turns alternate. The object of the game is to capture all 12 of the opponent's pieces; or, if no further captures are possible, to have more pieces remaining than the opponent. Pieces always rest on the points of intersection of the board's grid lines. On a turn, a player either moves one of their pieces a single step in any direction (forwards, backwards, sideways, or diagonally) to an unoccupied point, or makes a ''capturing'' move special to Surakarta.Capturing move
A capturing move consists of traversing along an inner or outer circuit (coloured blue and green in the diagram, but red and blue in the photo) around at least one of the eight corner loops of the board, followed by landing on an enemy piece, it. Captured pieces are removed from the game. Corner loops are used only when making a capture. The capturing piece enters and leaves the circular loop via a grid linetangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More ...
to the circle. Any number of unoccupied points may be travelled over, before or after traversing a loop. An unoccupied point may be travelled over more than once during the capturing piece's journey. Only unoccupied points may be travelled over; jumping over pieces is not permitted.
Capturing is always optional (never mandatory).
End of game
A game is won when a player captures all 12 of the opponent's pieces. If neither side can make headway, the game is ended by agreement and the winner is the player with the greater number of pieces in play.Scoring
A match consists of more than one game. Players agree beforehand how the winner will be determined. A couple of methods are typically used: * ''Playing a fixed number of games:'' Each game is scored by the number of pieces in play at the end of the game. The winner is the player with higher total points after all games have finished. * ''Playing to a fixed number of points:'' New games are played until one player reaches or exceeds the winning point total.Strategy
In general, pieces are more powerful toward the centre of the board, where they are in one or two sets of loops. Pieces on the corner, on the other hand, are easy to trap, as the spaces next to the corner can be attacked in a number of directions.Computer opponents
Surakarta is one of the games played regularly at the annualComputer Olympiad
The Computer Olympiad is a multi-games event in which computer programs compete against each other. For many games, the Computer Olympiads are an opportunity to claim the "world's best computer player" title. First contested in 1989, the majori ...
.
Variants
Surakarta variants are also played inrural China
Rural society in the People's Republic of China encompasses less than half of China's population (roughly 45%) and has a varied range of standard of living and means of living. Life in rural China differs from that of urban China. In Northern and ...
and Korea, with slightly different rules and boards. In these variants, pieces cannot step diagonally, and can slide along the outer circuit without capturing a piece.
A 7x7 grid variant with 14 pieces for each player is played in Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta (; jv, ꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠ ; pey, Jogjakarta) is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, ...
, Java, Indonesia and is called Bas-basan sepur. Whereas the game Surakarta is smaller with a 6x6 grid and only 12 pieces, but both games have the two capturing circuits (inner and outer circuits), and employ the same rules. Bas-basan sepur today is rarely known in Yogyakarta with only 5.6% of participants in one 2016 survey showing knowledge of the game. Questionnaires were provided by Kinderstation International of which most of the participants surveyed were in Yogyakarta specifically with students mostly between the grades 4-6 in SD Muhamadiyah Condong Chess and Schools. Back in the 1980s the game was played often in some areas of Yogyakarta (such at the Imogiri
Imogiri (ꦲꦶꦩꦒꦶꦫꦶ in Javanese script or ''Imagiri'' in standard Javanese spelling) is a royal graveyard complex in Yogyakarta, in south-central Java, Indonesia, as well as a subdistrict under the administration of Bantul Regency. Im ...
and Bantul
Bantul is a town and district, and the capital of Bantul Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The district (''kapanewon'') covers an area of and had a population of 64,360 at the 2020 Census. It is a bustling town about to the sout ...
areas).
Notes
References
Bibliography * * * *External links
* Surakarta printable board https://sites.google.com/view/cavegames-surakarta/home *{{bgg, 13715, SurakartaSurakarta
for Android
Khamadi et al, Perancangan Konsep Adaptasi Permainan Tradisional Bas-Basan Sepur Dalam Permainan Digital "Amukti Palapa"
Abstract strategy games Traditional board games Indonesian inventions Indonesian traditional games